How to Troubleshoot and Fix Common SMTP Email Error Codes
Introduction
When sending emails, encountering bounce codes is common. These codes indicate why an email failed to reach the recipient and provide guidance on how to fix the issue. Understanding and troubleshooting these errors can improve email deliverability, prevent spam filtering, and ensure effective communication with your audience.
This guide will break down four of the most common email bounce codes, explain their causes, and provide step-by-step solutions to resolve them.
1. SMTP Error Code: 550 no mailbox by that name is currently available
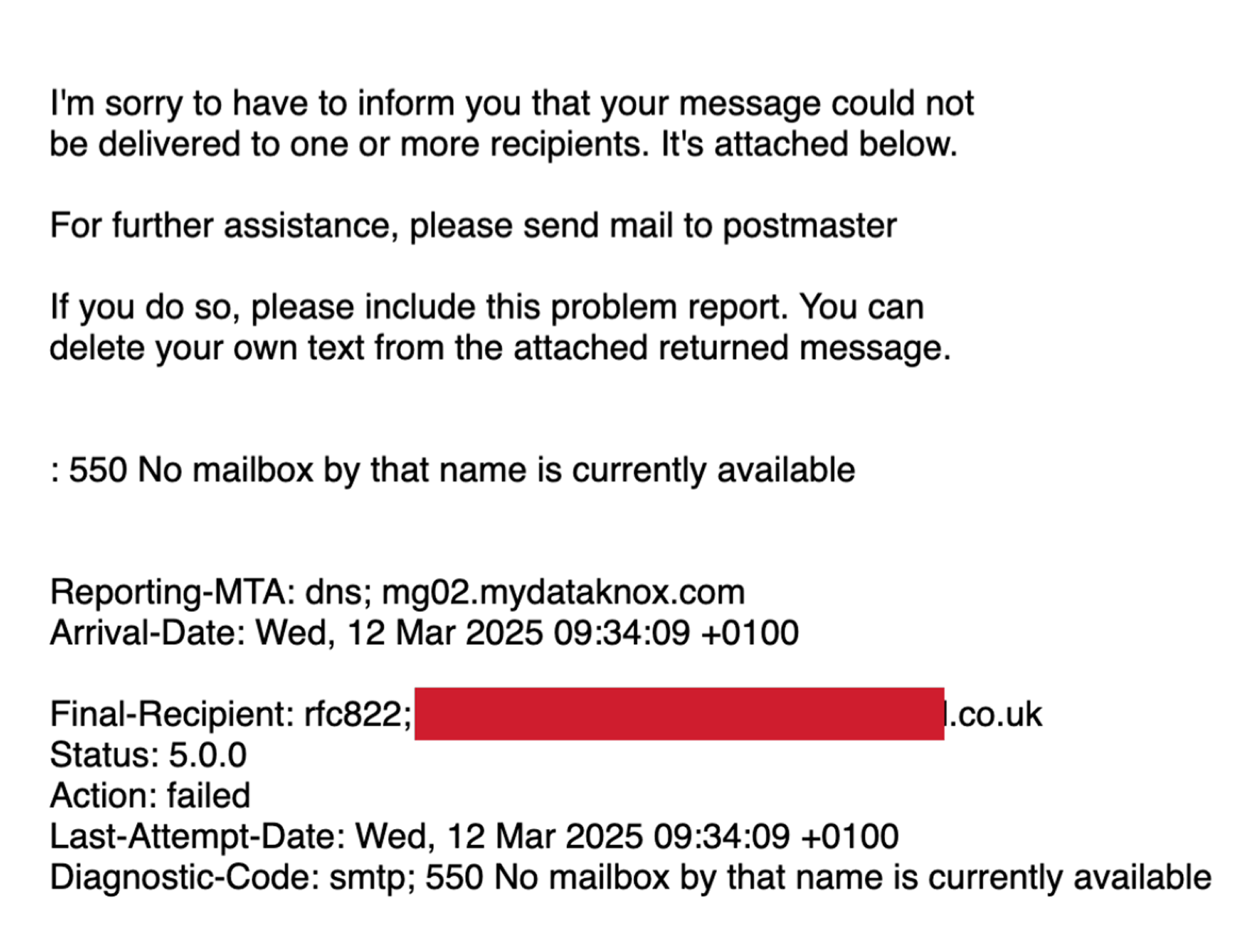
What It Means
The 550 No mailbox by that name error usually indicates that the recipient’s email address does not exist or has been deactivated. This may be due to a typo, an outdated email address, or the recipient deleting their account.
How to Fix It
- Verify the Email Address: Double-check the spelling of the email address for typos or missing characters.
- Confirm with the Recipient: If the address looks correct but still bounces, contact the recipient through another channel to confirm if the address is still active.
- Use Email Verification Tools: Services like ZeroBounce, Hunter, or NeverBounce can validate email addresses before sending emails.
Pro Tip
Before launching email campaigns, regularly clean your mailing list to remove invalid or inactive addresses. This reduces bounce rates and improves sender reputation.
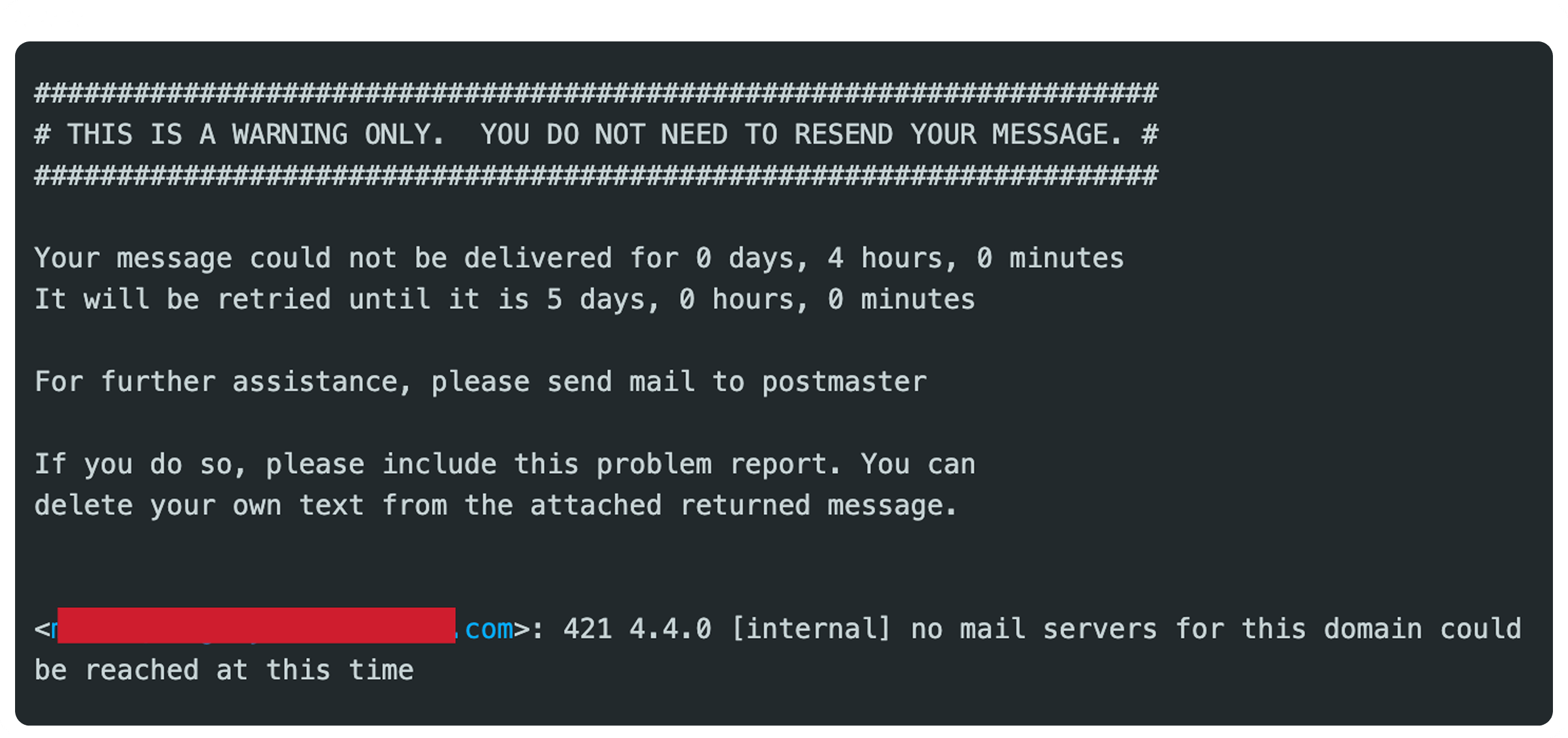
2. SMTP Error Code: 421 4.4.0 [internal] no mail servers for this domain could be reached
What It Means
The 421 4.4.0 [internal] no mail servers for this domain could be reached error occurs when the recipient’s email server is temporarily down or when there are issues with its Mail Exchange (MX) records.
How to Fix It
- Wait and Retry: Since this is often a temporary issue, wait a few hours and attempt to resend the email.
- Check MX Records: Use online tools like MXToolbox to verify the recipient’s domain has the correct MX records and is operational.
- Contact the Recipient’s IT Department: If the issue persists, inform the recipient so their IT team can investigate potential server or domain configuration issues.
Pro Tip
If a particular domain frequently returns this bounce code, it may be experiencing ongoing technical problems. Keep a record of repeated bounces and notify affected recipients.
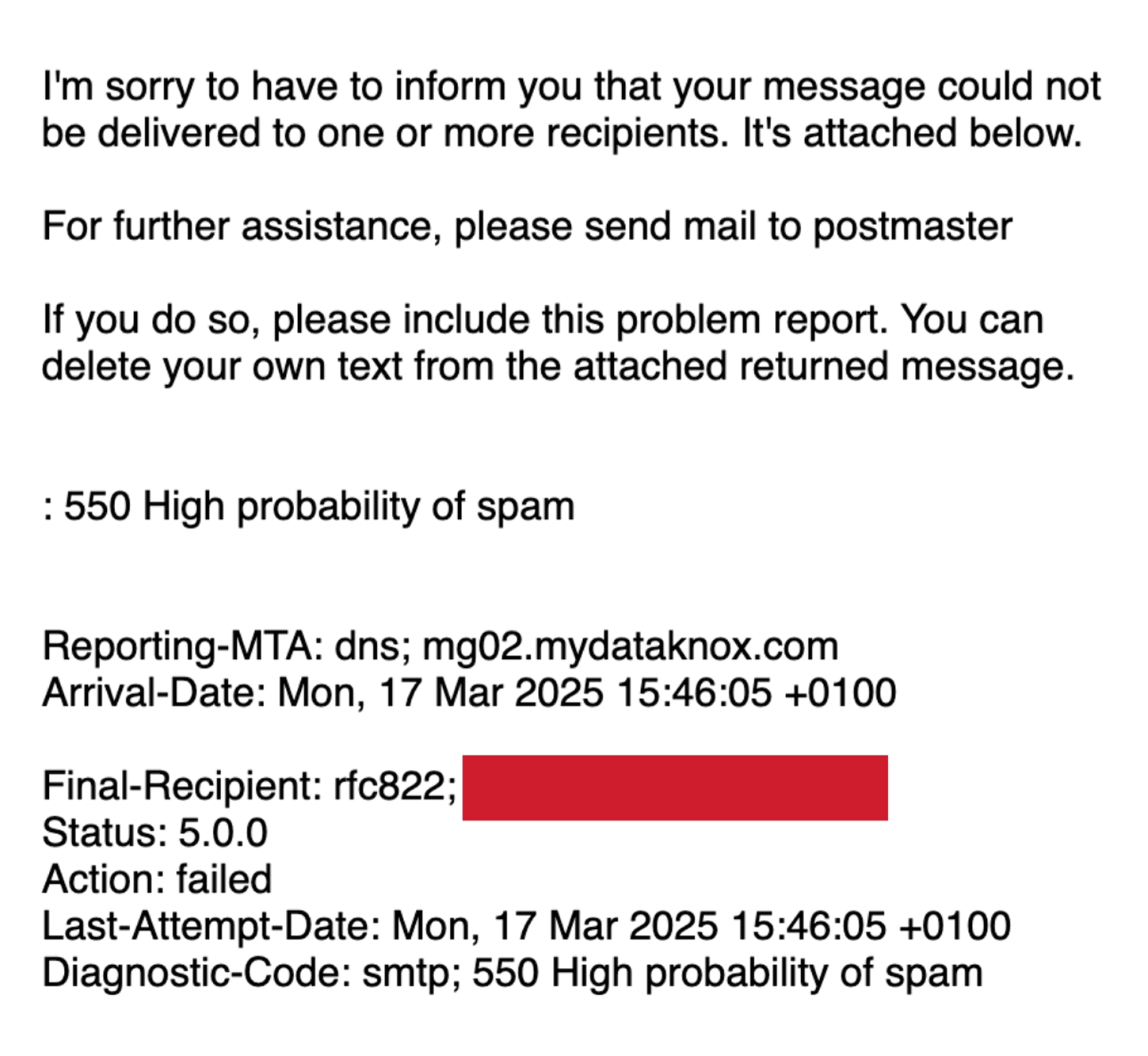
3. SMTP Error Code: 550 High Probability of Spam
What It Means
The 550 High probability of spam error means the recipient’s mail server flagged your email as spam. This can happen due to missing authentication records, poor email content, or an unreliable sender reputation.
How to Fix It
Set Up Email Authentication: Ensure proper configuration of:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Prevents spoofing by verifying sender IPs.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Adds a digital signature to emails for authenticity.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): Defines how email providers should handle unauthenticated messages.
Improve Email Content:
- Avoid using excessive capital letters, exclamation marks, or overly promotional language.
- Reduce the number of links and attachments.
- Personalize emails instead of sending generic mass emails.
Switch to SMTP Port 587:
- Many email providers block or restrict traffic on SMTP port 465 due to spam concerns.
- Port 587 supports STARTTLS encryption, improving deliverability and security.
Pro Tip
Use email testing tools like Mail-Tester to analyze your email’s spam score before sending it.
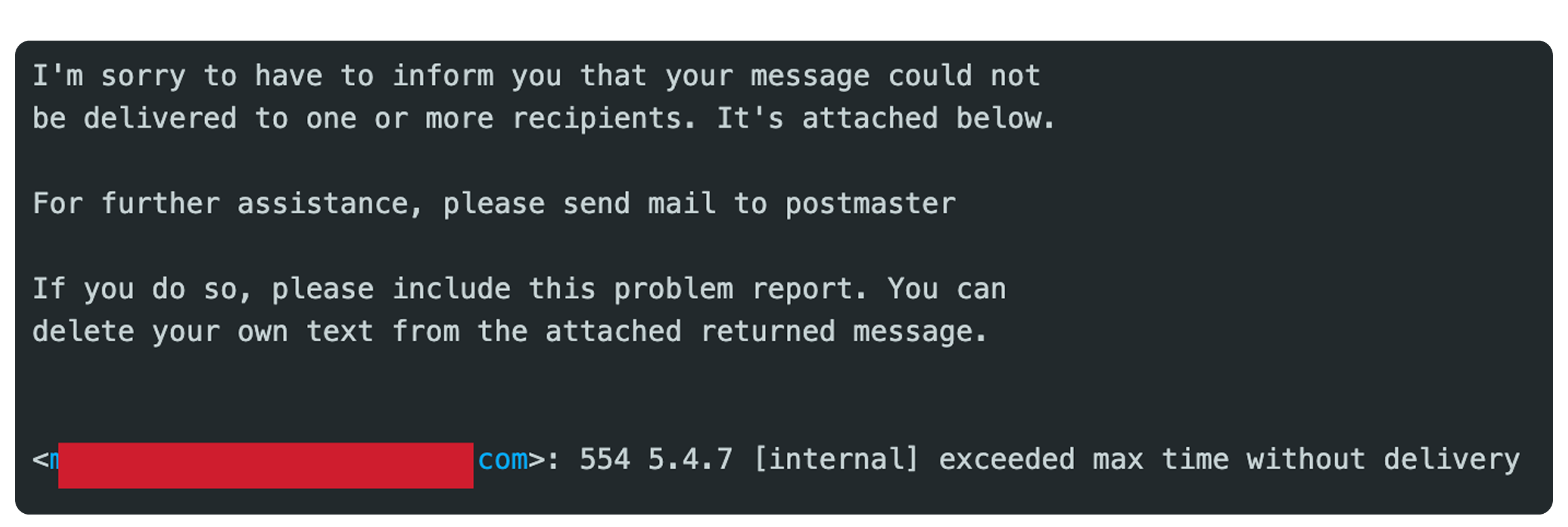
4. SMTP Error Code: 554 5.4.7 [internal] exceeded max time without delivery
What It Means
The 554 5.4.7 [internal] exceeded max time without delivery error occurs when the recipient’s server fails to deliver the email within its allowed time frame. This usually happens due to:
- Server congestion.
- Email routing issues.
- Blocked messages due to security filters.
How to Fix It
- Retry Sending Later: Wait and attempt to resend the email after some time.
- Monitor Your Own Server Load: Ensure your mail server is functioning properly and not experiencing delays.
- Check Email Queues: If using an email service provider, review email logs to identify recurring issues.
Pro Tip
If this bounce code happens frequently, consider contacting your email provider to ensure proper email routing and delivery processes.
5. SMTP Port 587: A Crucial Fix for Email Deliverability
Why It Matters
Switching to SMTP port 587 helps resolve multiple email delivery issues, including:
- Spam filtering problems.
- Authentication failures.
- Server connection errors.
When to Use SMTP Port 587
- If emails are frequently being flagged as spam or not delivered.
- If you are currently using outdated ports (e.g., port 465).
- If your email service provider recommends a secure connection.
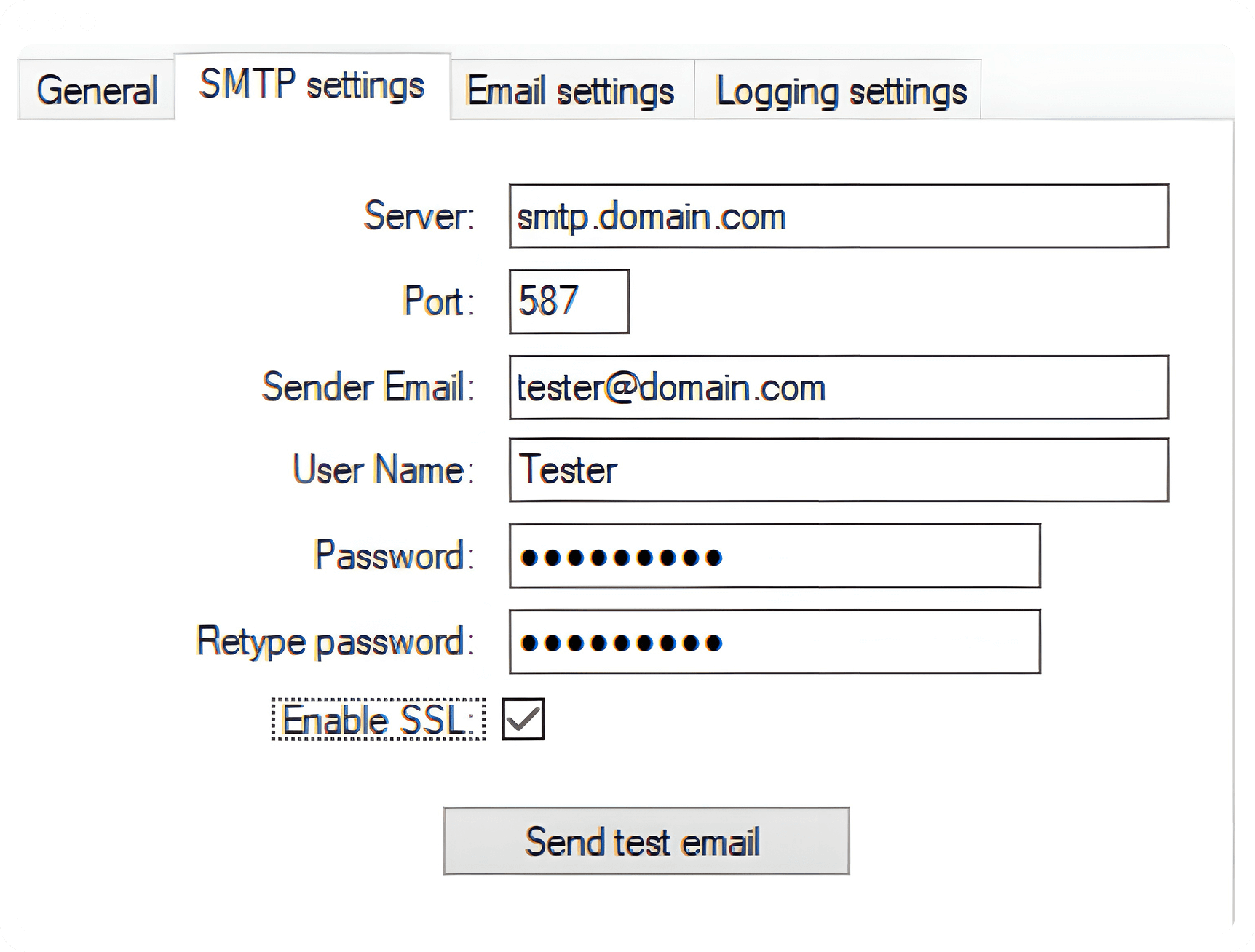
How to Switch to Port 587
- Access your email client settings.
2 Locate the Outgoing Server (SMTP) Settings. - Change the port to 587 and enable STARTTLS encryption.
- Save the changes and test sending an email.
Final Thoughts: How to Resolve Email Bounce Codes Effectively
When dealing with email bounce codes, the key is to identify the issue based on the specific error message and take appropriate action.
Quick Recap of Fixes:

By implementing these solutions, you can minimize email bounces, improve deliverability, and maintain a healthy sender reputation.
Need Help?
If your emails are still bouncing despite these fixes, consider consulting an email deliverability expert or using an email service provider with built-in optimization features.
With the right troubleshooting steps, you can ensure that your emails reach their intended recipients, maximizing engagement and response rates.